Automation offers cost-effective, sustainable solutions for unlocking revenues and delivering better patient financial experiences (Part 1 of 2).
Clinical staff shortages are much discussed, many providers also lack staff in their revenue cycle operations. That’s creating major bottlenecks in claims submission and follow-up. A survey of 205 CFOs and vice presidents of revenue cycle found that 48% of organizations were experiencing a “severe” labor shortage in revenue cycle operations, with another 34% reporting a “moderate” shortage.
That makes the timing right for healthcare providers to take advantage of automation technology, ranging from robotic process automation (RPA) to AI and machine learning (ML) models. Automation gives healthcare providers the opportunity to streamline key RCM workflows and avoid high labor costs, increase financial flexibility, improve work satisfaction rates and deliver better patient experiences. In this article, we explain how healthcare providers are using automation to solve RCM and related issues. In Part 2, we offer guidelines for choosing business cases and technology to help ensure automation delivers real results.
Quickly unlocking revenue with robotic process automation
Many of the tasks across the RCM value chain are excellent candidates for automation. Those that are largely standardized, rote and repetitive are ideal for RPA, automation achieved with software bots. These bots can be trained to do the keystrokes that humans do, even when the execution functions are in different software applications. Instead of having your well-paid RCM specialist call a health insurer about a claim’s status, a bot can easily look up this information on a payer website and portal. The skilled individual is then free to work on more complex claims. The bots can work tirelessly while reducing costs, improving quality of service and improving cash flow.
Some examples:
Claims status: We worked with a large healthcare system in the southeastern U.S. that had traditionally used a manual process for checking claims status. A labor shortage had led to a backlog of more than 5, 000 claims representing about $5 million in revenue with just one of its payers. We estimated it would take approximately 109 workdays for humans to address these. Within six weeks, we had developed a bot. Deployed on a Saturday morning, by Saturday evening the bot had cleared the claims backlogfor that payer. It was then a relatively quick process to adapt the solution to additional payers, including Medicaid and Medicare.
The bot development can take place offshore, eliminating half or more of the development costs, while deployment onshore alleviates compliance concerns. For our southern healthcare provider client, the bots do not displace any employees but are filling gaps left by the labor shortage and freeing remaining employees to do more valuable work. Before the automation, it took more than 40 FTE to complete the claim status checks; now fewer than 10 can accomplish the same volume. The organization also is saving $350, 000 annually.
Automated patient pre-registration. This more complex application we built for a large mid-southern hospitalincorporates RPA along with patient self-service features and the provider’s back office. When a patient agrees to interact digitally with the provider, RPA bots download patient registration requests; retrieve patient data from the electronic health record (EHR); then update the patient engagement system. That triggers the engagement system to send the patient a self-registration and payment link. When the patient has completed those steps, the RPA bots then access the payment and patient demographic data and update the provider’s EHR.
The RPA bots have contributed to the provider’s 85% improvement in pre-registration cash collection, representing an overall increase of $5.45 million. Patient engagement improved 25% while costs to collect decreased.
- Digitally enabled prior authorization. With regulators increasingly focused on preauthorization, this process is ripe for automation. Bots can easily retrieve patient data, insurance details, CPT codes, physician details, diagnosis codes and schedules from an EHR; flag cases requiring prior authorization; and submit them digitally to a payer portal. Then bots can update records with approved requests. They can also automatically route denied cases requiring additional information to the right clinicians, then refile them when updated.
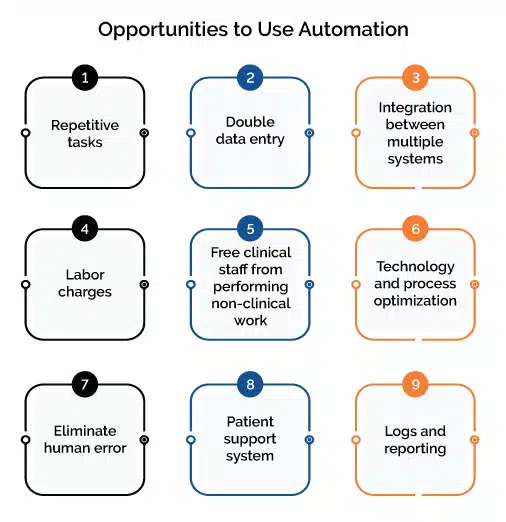
Advancing automation for more sophisticated RCM applications
Software bots are the simplest and often the most cost-effective automation, even for processes that involve multiple steps or a lot of human and machine interaction. More sophisticated automation solutions built on AI and ML models can tackle more complex tasks that can involve business rules and decisions based on the models’ data analysis. These can help improve the patient’s experience while minimizing provider labor effort and costs. However, the initial tradeoff is that these AI/ML solutions often are more expensive and take longer to implement. That said, for providers with some automation maturity, these can make sense.
The value of automation is undeniable. In addition to accelerating the revenue cycle, automation can create more of the digital efficiency and self-service options healthcare consumers want. But healthcare providers must choose their automation cases wisely to get the returns on investment they expect. We’ll cover how to choose in Part 2.
For additional information or questions on how Firstsource can help your organization leverage automation across the revenue cycle, please contact Angela Billet, SVP Strategic Provider Accounts or Vimal Nagarajan, VP Technology.